
Arbor Assays Oxidative Stress Assay Kits
什么是氧化应激?
氧化应激被广泛定义为活性氧(ROS)或自由基的产生与细胞抗氧化防御的消除之间的不平衡。不受控制的氧化应激的后果可能导致对对细胞结构和功能至关重要的生物分子的氧化损伤。1,2
幸运的是,强大的氧化应激反应机制已经进化,以保护生物体免受生物系统中氧化压力的破坏性影响。然而,不受控制的氧化应激与多种病理生理学和与年龄相关的疾病有关,了解氧化应激在健康和疾病中的作用是许多生物医学研究计划的共同目标。3
Arbor Assays提供了测量关键氧化应激生物标志物的状态和活性的工具。例如,我们的谷胱甘肽和过氧化氢检测试剂盒是最简单、最灵敏的检测试剂盒,可帮助研究人员更好地监测氧化应激的机制和反应。
氧化应激相关试剂盒:
| 过氧化氢酶(CAT)荧光法活性试剂盒 | |
| 铜蓝蛋白(CP)比色活性试剂盒 | DNA损伤ELISA试剂盒 |
| Formaldehyde Fluorescent Detection Kit | FRAP™ (Ferric Reducing Antioxidant Power) Detection Kit |
| Glutathione (GSH) Colorimetric Cuvette Detection Kit | Glutathione (GSH) Colorimetric Detection Kit |
| Glutathione (GSH) Fluorescent Detection Kit | Glutathione (GSH) Fluorescent Detection Kit (384-Well Plate) |
| Glutathione Reductase (GR) Fluorescent Activity Kit | Glutathione S-Transferase (GST) Fluorescent Activity Kit |
| Hemoglobin Colorimetric Detection Kit | Hemoglobin High Sensitivity Colorimetric Detection Kit |
| Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) Colorimetric Detection Kit | Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) Fluorescent Detection Kit |
| Myeloperoxidase (MPO) Human ELISA Kit | Nitric Oxide (NO) Colorimetric Detection Kit |
| Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) Colorimetric Activity Kit | TBARS/MDA Universal Colorimetric Detection Kit |
| Thiol Fluorescent Detection Kit |
Oxidative Stress FAQs
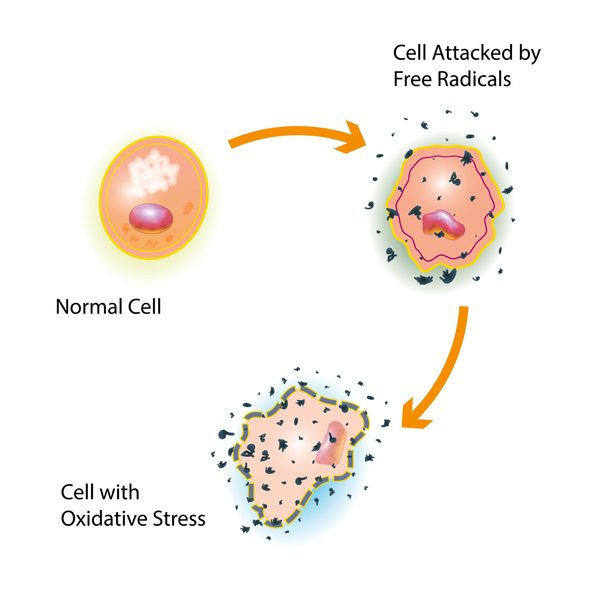 What are free radicals?
What are free radicals?
Free radicals, including reactive oxygen species (ROS), are molecules with one or more unpaired electrons. Production of free radicals is a normal part of life, and moderate concentrations are involved in a number of signaling pathways, synthesis of cellular structures, and host defense against pathogens. Free radicals arise as byproducts of normal metabolic processes or from external sources such as radiation, cigarette smoke and pesticides.
Excessive or unchecked ROS production can cause cellular damage and is implicated in a variety of pathologic and age-related conditions. Examples of potentially damaging free radicals include:
Superoxide (O2-•),
Hydroxyl radical (•OH)
Nitric oxide radical (NO)
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2),
Biological systems produce free radicals during normal metabolic processes, and cells also produce antioxidants that neutralize excess free radicals. Under normal circumstances, the body is able to maintain a balance between antioxidants and free radicals.
Excessive oxidative stress can lead to an imbalance of free radicals and antioxidants. Subsequent oxidative damage occurs to proteins, lipids, and DNA, which could lead to cytotoxicity, genotoxicity, and even carcinogenesis when damaged (mutated) cells proliferate. Uncontrolled oxidative stress can accelerate the aging process and may contribute to the development of a number of pathologic conditions.
Several factors contribute to oxidative stress and excess free radical production including diet, lifestyle, and environmental conditions. The body’s natural immune response can also trigger oxidative stress temporarily. This type of oxidative stress causes mild inflammation while the immune system fights off infection or repairs an injury.
Antioxidants are substances that neutralize or remove free radicals by donating an electron. The neutralizing effect of antioxidants helps protect biological systems from oxidative stress. Examples of antioxidants include vitamins A, C, and E. Cells can also produce endogenous antioxidants such as glutathione (GSH).
Oxidative stress that results from physical activity has beneficial, regulatory effects on the body. Free radicals formed during physical activity regulate tissue growth and stimulate the production of antioxidants. Mild oxidative stress may also protect the body from infection and diseases.
However, long-term uncontrolled oxidative stress damages the body’s cells, proteins, and DNA. This can contribute to aging and may play an important role in the development of a range of conditions. Most notably, oxidative stress can cause chronic inflammation. Under normal circumstances, infections and injuries trigger the body’s immune response producing free radicals while fighting off invading germs. These free radicals can also damage healthy cells, leading to inflammation. Oxidative stress can also trigger the inflammatory response, which produces more free radicals leading to further oxidative stress, creating a cycle. Chronic inflammation from oxidative stress may lead to several conditions, including neurodegenerative diseases, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and arthritis.
Oxidative stress may play a role in the development of a range of conditions, including:
Cancer
Alzheimer’s disease
Parkinson’s disease
Diabetes
Cardiovascular conditions such as high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, and stroke
Inflammatory disorders
Chronic fatigue syndrome
Asthma
Male infertility
Understanding the role ROS play in health and disease is a common goal of many biomedical researchers. The level of oxidative stress can be determined by measuring the quantity of free radicals, ROS, antioxidants, or the activity of cellular mechanisms deployed to control levels of oxidative stress. Arbor Assays offers a variety of oxidative stress kits to help answer your most challenging questions about oxidative stress mechanisms.
Betteridge, D. J. (2000). What is oxidative stress? Metabolism, 49, 3–8.
Sies, H., & Jones, D. P. (2007). Oxidative stress. Encyclopedia of Stress, 45–48.
Liquori, I., et al. (2018). Oxidative stress, aging, and diseases. Clinical Interventions in Aging, 13, 757–772.
ARBOR ASSAYS KITS FOR YOUR RESEARCH – EXPECT ASSAY ARTISTRY
▪ 所有产品均在密歇根州安阿伯开发和制造
▪ 每个试剂盒最多进行过200次质量分析
▪ 按照美国或国际标准校准